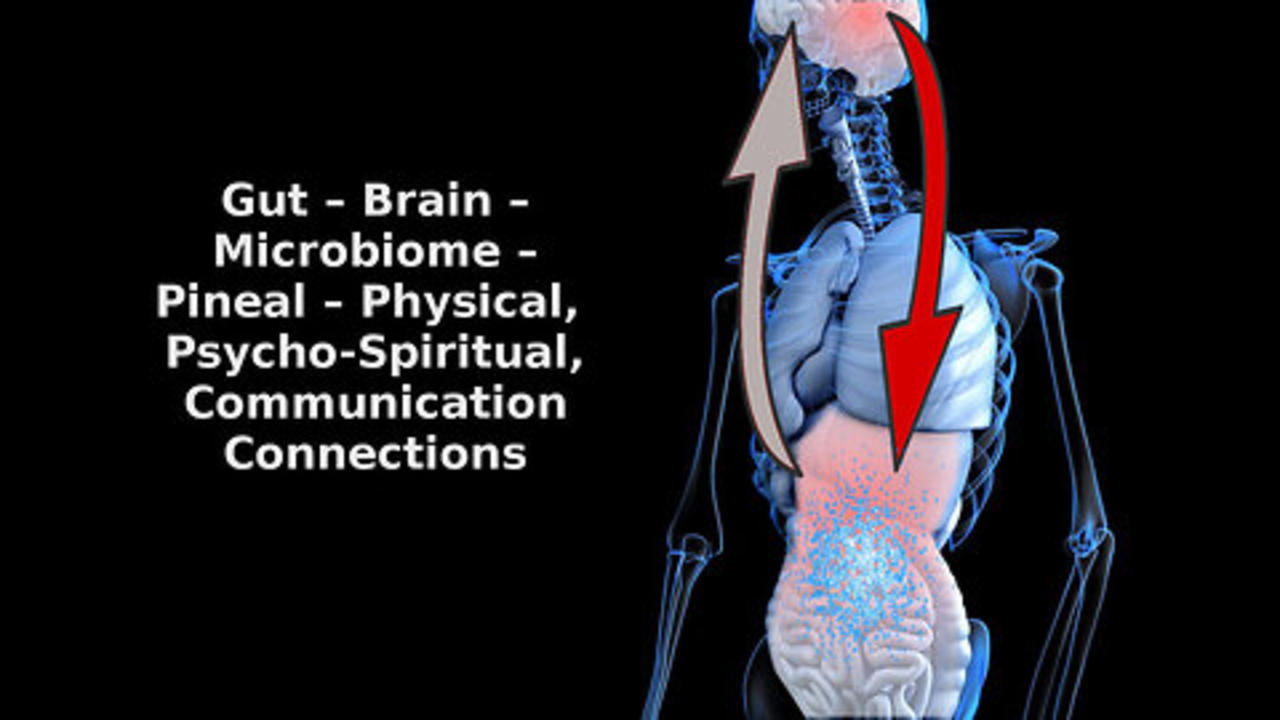
First, the gut is often referred to as the "second brain" because it contains a complex network of nerves and cells called the enteric nervous system (ENS) that communicates with the brain.
The ENS controls various aspects of digestion, including swallowing, enzyme release, blood flow regulation, and elimination.
It plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption and overall digestive function.The gut and the brain are in constant communication through a process called crosstalk.
The gut sends signals to the brain, and the brain sends signals back to the gut.
This communication affects how we feel and perceive gastrointestinal symptoms. The gut-brain connection is also linked to mental health.
The ENS communicates with the brain through hormones, the immune system, and microorganisms in the gut.
Research suggests that disruptions in the gut-brain axis may contribute to certain diseases and mental health conditions.Certain foods can help improve gut health and mood.
Incorporating fiber-rich, probiotic-rich, and prebiotic-rich foods, omega-3 fatty acids, and fruits and vegetables into your diet can help improve gut health and mood.
It's important to note that food should not be the only treatment for mood disorders, and it's essential to seek professional help if you are experiencing severe symptoms.Other important facts about gut health include the impact of stress on gut health, the importance of prebiotics and probiotics, and the influence of the gut microbiota on mood and emotions.
Understanding these facts about gut health can help emphasize the importance of maintaining a healthy gut through a balanced diet, managing stress, and incorporating prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods into your routine.
